Detection and Management of Amyloid-Related Imaging Abnormalities During Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment
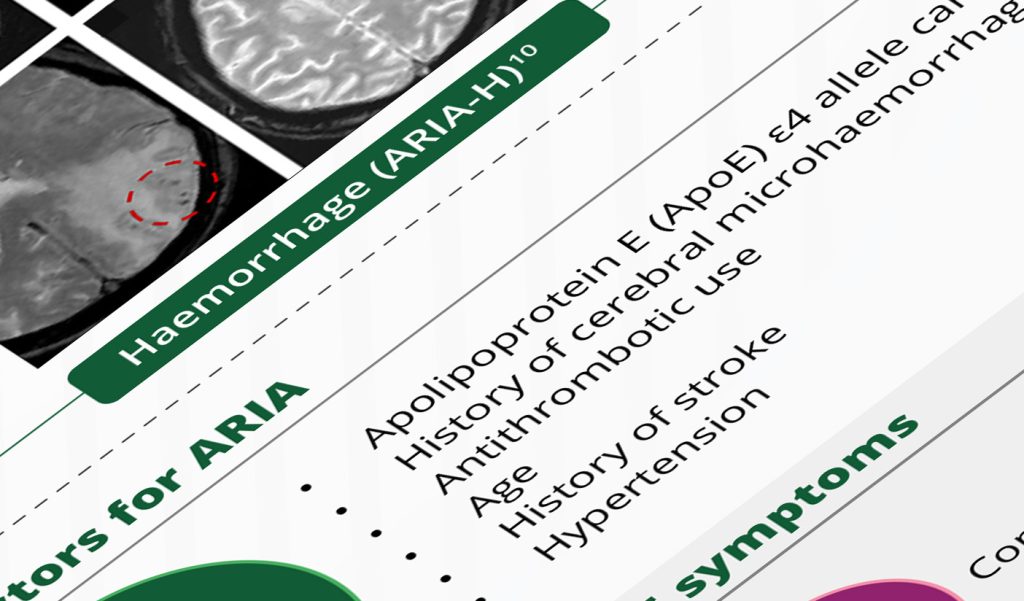
• Challenges in detecting ARIA clinically
• Clinical progression of ARIA
• Standard MRI protocol for ARIA detection
• Anti-amyloid therapy and ARIA
• Strategies for managing ARIA and the role of healthcare professionals
• Clinical progression of ARIA
• Standard MRI protocol for ARIA detection
• Anti-amyloid therapy and ARIA
• Strategies for managing ARIA and the role of healthcare professionals
Mapping the Future: Disease-Modifying Treatments for Alzheimer’s
Our infographic reveals how Disease-Modifying Therapies (DMTs) are revolutionizing Alzheimer's Disease care. It highlights the urgent need for novel biomarkers that enable non-invasive, high-throughput detection of pre-symptomatic AD, significantly enhancing diagnostic capabilities. The infographic also emphasizes the importance of education and training in establishing new care pathways, ensuring the safe and efficient delivery of treatments. Additionally, it explores the crucial role of real-world data in advancing treatment strategies. Click to explore these transformative insights and learn how they are shaping the future of Alzheimer's care.
Pathway to Accurate Alzheimer’s Diagnosis
• Pathophysiology of AD
• Challenges in diagnosing AD
• Collaborative strategies to enhance diagnostic accuracy
• Challenges in diagnosing AD
• Collaborative strategies to enhance diagnostic accuracy
The Current Treatment Landscape of Alzheimer’s Disease
• Understanding the clinically meaningful benefits of treatments for Alzheimer’s disease (AD)
• Monoclonal antibodies targeting amyloid β in AD
• Collaborative and equitable dementia care
• Prevention potential of AD
• Monoclonal antibodies targeting amyloid β in AD
• Collaborative and equitable dementia care
• Prevention potential of AD
Navigating Alzheimer’s Disease
Explore our infographic on Alzheimer's disease diagnosis and care. Learn about symptoms, differential diagnosis, and criteria, with a spotlight on biomarkers and imaging. Further your knowledge about amyloid-targeted therapies for early AD, managing Amyloid-Related Imaging Abnormalities (ARIA), and current treatment guidelines for comprehensive patient support.
Overview of disease continuum and early diagnosis
• Outline of clinical stages associated with AD.
• AD continuum and pathophysiological changes associated with AD progression.
• Emphasizes the need and barriers of early diagnosis of AD.
• AD continuum and pathophysiological changes associated with AD progression.
• Emphasizes the need and barriers of early diagnosis of AD.